How to setup GitLab Runner on Kubernetes Cluster
GitLab Runner is a powerful tool that improves the development process, particularly for teams already using GitLab. In this article, we'll elaborate how to install GitLab Runner on Kubernetes Cluster
Introduction
GitLab Runner is a powerful tool that improves the development process, particularly for teams already using GitLab. This article provides an in-depth look at GitLab Runner, its benefits, capabilities, and a comparison with other tools like Jenkins. We'll also explore the different executor types of GitLab Runner and how to choose the right one for your project.
About 8grams
We are a small DevOps Consulting Firm that has a mission to empower businesses with modern DevOps practices and technologies, enabling them to achieve digital transformation, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
Ready to transform your IT Operations and Software Development processes? Let’s join forces and create innovative solutions that drive your business forward.
What is GitLab Runner?
GitLab Runner is an open-source application used for running Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) jobs in the GitLab environment. It works with GitLab CI/CD to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software applications. GitLab Runner acts as an agent that listens for instructions from GitLab CI/CD, executes the specified tasks, and reports the results back to GitLab.
GitLab and GitLab Runner
When a development team is already using GitLab, integrating GitLab Runner provides the following benefits:
Seamless integration: GitLab Runner is designed to work in harmony with GitLab, ensuring smooth coordination between the two systems.
Simplified workflow: By using GitLab Runner, developers can consolidate their code repository, issue tracking, and CI/CD pipelines within the same platform, streamlining the development process.
Improved collaboration: GitLab Runner facilitates effective communication among team members by providing real-time feedback on the status of builds, tests, and deployments.
Scalability: GitLab Runner allows for scaling CI/CD infrastructure to meet the demands of large projects and teams.
Capabilities
GitLab Runner provides several capabilities, including:
Cross-platform support: GitLab Runner can run on various platforms, including Linux, macOS, Windows, and Kubernetes.
Multiple executors: GitLab Runner supports multiple executors, such as Docker, Kubernetes, Shell, and more, providing flexibility in choosing the right execution environment.
Parallel execution: GitLab Runner can run multiple jobs concurrently, speeding up the overall CI/CD process.
Advanced caching: GitLab Runner offers advanced caching mechanisms to optimize build times.
GitLab Runner Executors
GitLab Runner supports various executors, each with its unique advantages, allowing developers to choose the right execution environment for their projects. Here's a detailed overview of each executor:
Shell Executor
The Shell executor runs builds directly on the host where the GitLab Runner is installed. It is the simplest and quickest executor to set up, requiring minimal configuration. However, it may not be the most suitable choice for complex projects that need isolated environments or when multiple projects are running on the same host.
Advantages:
Easy to set up and configure
Low resource overhead
Direct access to the host's file system and services
Disadvantages:
Limited isolation between build environments
Increased risk of conflicts between projects sharing the same host
Docker Executor
The Docker executor runs builds inside Docker containers, offering better isolation and consistency across different environments. It is highly recommended for projects that require a clean, reproducible environment for each build. However, it requires Docker to be installed and configured on the host system.
Advantages
Improved isolation between build environments
Consistent build environments
Simplified management of dependencies
Disadvantages
Requires Docker to be installed and configured
Additional resource overhead due to containerization
Kubernetes Executor
The Kubernetes executor runs builds on a Kubernetes cluster, providing excellent scalability and resource management. It is the ideal choice for teams that already have a Kubernetes infrastructure in place or require dynamic scaling of build resources.
Advantages
Scalability and efficient resource management
Isolation of build environments
Integration with Kubernetes-native features
Disadvantages
Requires a Kubernetes cluster to be set up and configured
Steeper learning curve for teams unfamiliar with Kubernetes
Parallels Executor
The Parallels executor is designed for macOS systems and runs builds inside Parallels Desktop VMs. It is particularly useful for macOS-based projects that require isolation between build environments or when testing applications across different macOS versions.
Advantages
Isolation between build environments on macOS systems
Allows testing across different macOS versions
Disadvantages
Requires Parallels Desktop to be installed and configured
Limited to macOS systems
Additional resource overhead due to virtualization
SSH Executor
The SSH executor runs builds on remote servers over SSH. It is useful when there is a need to execute CI/CD tasks on a specific server or when you want to offload build tasks from the GitLab Runner host.
Advantages
Offloads build tasks to remote servers.
Suitable for projects that require a specific server environment.
Disadvantages
Requires configuration and management of remote servers.
Security concerns due to SSH access.
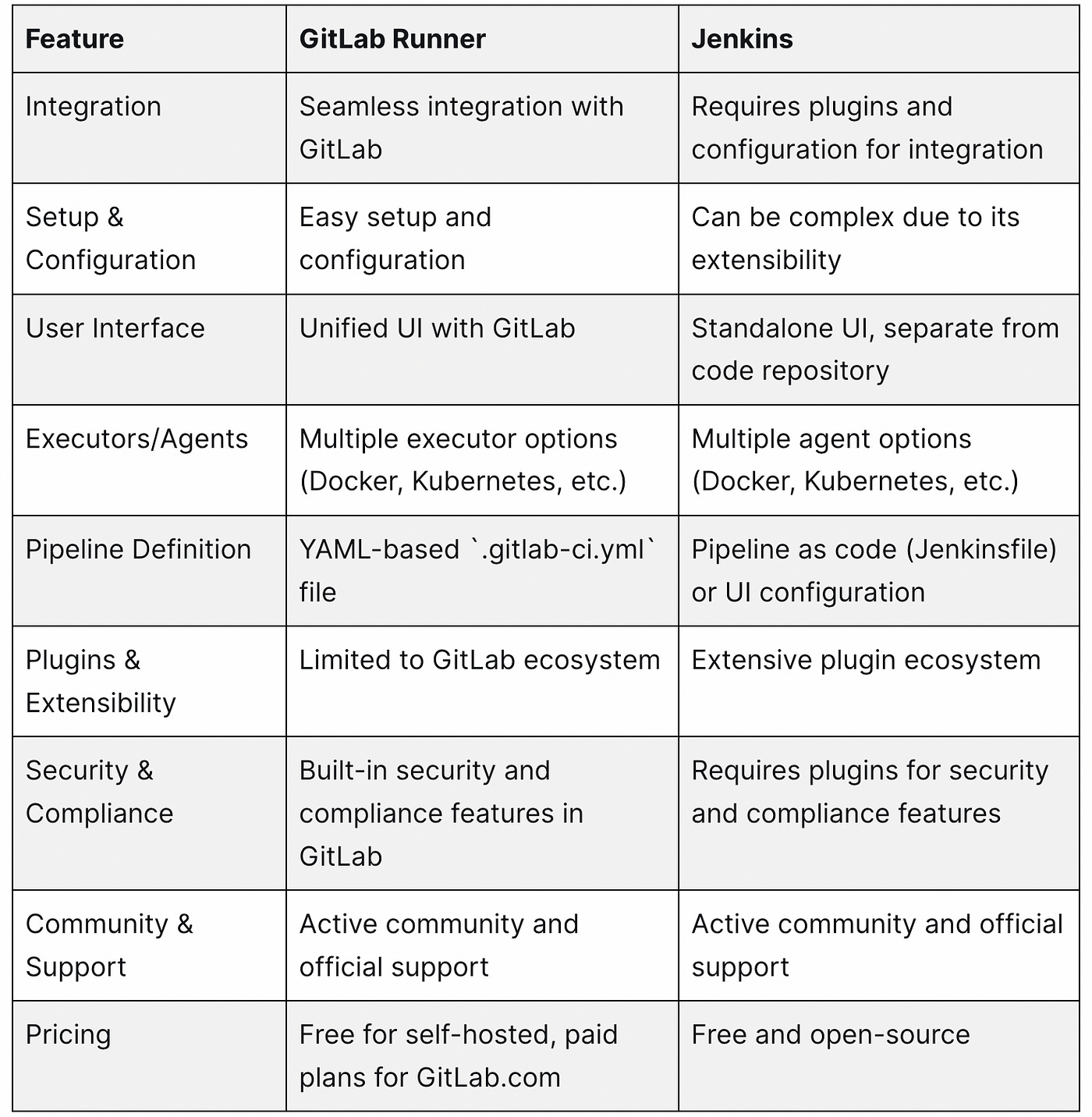
GitLab Runner vs Jenkins
In comparison, Jenkins is another popular CI/CD tool that has been widely used in the industry. While both GitLab Runner and Jenkins offer robust CI/CD features, GitLab Runner offers better integration and a more streamlined workflow with GitLab. Jenkins, on the other hand, provides a more extensive range of plugins and extensibility options.
Below is a comparison table of GitLab Runner and Jenkins, highlighting their main features, advantages, and disadvantages.
Both GitLab Runner and Jenkins are powerful CI/CD tools with robust features. GitLab Runner offers seamless integration and a more streamlined workflow with GitLab, while Jenkins provides an extensive range of plugins and extensibility options. The choice between the two tools ultimately depends on your team's needs, existing infrastructure, and familiarity with the respective platforms.
Setup GitLab Runner on Kubernetes Cluster
Before proceeding with the installation of GitLab Runner on your Kubernetes cluster, it's important to ensure that Helm is installed and properly configured. Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes, which simplifies the deployment and management of applications on a cluster.
In this guide, we will be using the official GitLab Runner Helm Chart.
~$ helm repo add gitlab https://charts.gitlab.io
~$ helm repo update gitlabWe recommend to create dedicated namespace for GitLab Runner
~$ kubectl create namespace gitlabCreate values.yaml for Helm installation
gitlabUrl: https://gitlab.example.com/
runnerRegistrationToken: "xxx"
concurrent: 10
checkInterval: 30
rbac:
create: true
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/exec"]
verbs: ["create"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/log"]
verbs: ["get"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/attach"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "create", "delete", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "create", "delete", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "create", "delete", "update"]
runners:
privileged: true
config: |
[[runners]]
[runners.kubernetes]
namespace = "gitlab"
tls_verify = false
image = "docker:19"
privileged = trueSome crucial details that need your attention are:
gitlabUrl: replace with your GitLab instance URL. If you use Gitlab.com, then the value should be
https://gitlab.com
runnerRegistrationToken: can be found on menu
CI/CD > Runnerprivileged: set
trueif you use docker-in-docker (dind)
Install with Helm
~$ helm install gitlab-runner gitlab/gitlab-runner -f values.yaml --namespace gitlabVerify Installation
~$ kubectl -n gitlab get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
gitlab-runner 1/1 1 1 42dAnd boom! You have scalable and reliable GitLab Runner running on your Kubernetes Cluster.